Matter
Properties of matter
Anything which has mass and occupies space is called matter. Everything around us, for example, book, pen. Pencil, water, air, all living beings etc. are composed of matter. You know that they have mass and they occupy space.
Matter can exist in three physical states viz. solid, liquid and gas. In solids, particles are held very close to each other in an orderly fashion and there is not much freedom of movement. In liquids, the particles are close to each other but they can move around better than in solids. However, in gases, the particles are far apart as compared to those present in solid or liquid states and their movement is easy and fast. Because of such arrangement of particles, different states of matter exhibit the following characteristics:
(i) Solids have definite volume and definite shape.
(ii) Liquids have definite volume but not the definite shape. They take the shape of the container in which they are placed.
(iii) Gases have neither definite volume nor definite shape. They completely occupy the container in which they are placed.
These three states of matter are inter convertible by changing the conditions of temperature and pressure. On heating a solid usually changes to a liquid. The liquid on further heating changes to the gaseous (or vapour) state. In the reverse process gas (or vapour) on cooling changes to liquid which on cooling changes to solid.
There is an important difference between gas and vapour which is shown below.
| Gas | Vapour |
| It exists in the single state | It exists as a combination of two states i.e. liquid, and gas. |
| It is a state of matter. | It is a transition state, not the state of matter. |
| These are formed during the boiling of liquid. | This is formed above the critical temperature of liquid, and below the critical pressure. |
A better understanding about matter is to know is as fallows.
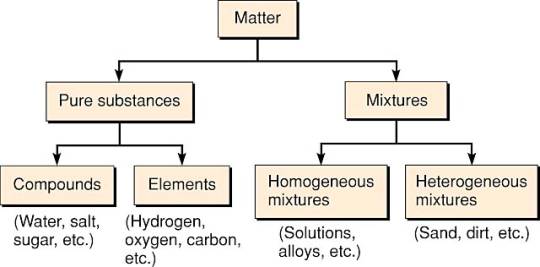
Element: The substances made up of only one type of atom are called elements.
The term element is introduced by ‘Robert Boyle’.
It cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means, and can exist as either atoms (e.g. argon) or molecules (e.g., nitrogen).
In the present time, element symbols and names are sanctioned by IUPAC; that is, International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. It should be noted that many symbols are usually the first one or two letters of their actual name in English. In addition, the first letter of a symbol would always be written in capital or uppercase.
Also, the second letter comes in small letter or lowercase. For example, Hydrogen H, Aluminium Al, and Cobalt Co. Furthermore, symbols for some elements are created from the first letter of their name together with a letter falling later in their name. For example, Chlorine, Cl and Zinc Zn.
There are symbols that have been picked from the names of elements mentioned in Latin, Greek or German. Just like the symbol for iron which is Fe and has a relation to its Latin name ferrum. So is the case for sodium (Na) natrium, as well as potassium (K) from kalium. Hence, each element possesses a name and an exclusive chemical symbol.
Note that most living matter consists primarily of the so-called bulk elements: oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur—the building blocks of the compounds that constitute our organs and muscles. These five elements also constitute the bulk of our diet; tens of grams per day are required for humans.
Carbon is the main element in organic compounds, so carbon is essential to life on Earth.
It is the fourth most abundant element in the universe, the fifteenth most abundant element on Earth, and the second most abundant element in the human body, after oxygen. Carbon is present in all known life forms. It can be found dissolved in all water bodies on the planet.
Oxygen is the most vital element to life on the planet Earth. It has an atomic number of 8 and it is a gas when it is at room temperature. Oxygen is by far the most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, making up nearly 46% of mass.
Silicon is second, nearly 28%, followed by aluminum (8%), iron (5%), magnesium (2%), calcium (4%), sodium (3%), and potassium (3%).
Scientists believe that about 25 of the known elements are essential elements in the human body. The following are their names and the percentage mentioned is approximate as all the humans are not alike.
Carbon (C), Oxygen (O), Hydrogen (H) and Nitrogen (N) – make up about 96% of the human body. These are termed as Big4. Ca, P, K, S, Na, Cl and Mg are major elements in the human body about 3.5%. The other elements which are trace elements about 0.5% in the human body are B, Cr, Co, Cu, F, I, Fe, Mo, Se, Si, Sn, V and Zinc.
Among the 118 elements, 98 occur naturally on Earth. 37 are radioactive. Ten of these elements occur in trace amounts: technetium (No. 43), promethium (61), astatine (85), francium (87), neptunium (93), plutonium (94), americium (95), curium (96), berkelium (97), and californium (98).
The first radioactive element historically is radium. Though it was Henri Becquerel that discovered radioactivity, it was Marie Curie who coined the term.
The first in the periodic table is Technetium by lowest number, smallest mass, and all isotopes radioactive.
Technetium (chemical symbol Tc) is a silver-gray, radioactive metal. It occurs naturally in very small amounts in the earth’s crust, but is primarily man-made. Technetium-99 is produced during nuclear reactor operation. Technetium was actually discovered — produced artificially — in 1937 by Perrier and Segre in Italy. It was also found in a sample of molybdenum that was bombarded by deuterons in a cyclotron.
The word atom is derived from greek word ATOMIO which means indivisible.
The term ‘atom’ is introduced by ‘John Dalton”.
An atom is the smallest particle of the element which may or may not have individual existence at the normal temperature of 00c and 760mm pressure (S.T.P or N.T.P). Some elements like Na, Ca, He etc., can remain in atomic state but some like Oxygen, Fluorine, Chlorine, Nitrogen etc., cannot be in atomic state so they exist as O2, F2, Cl2, and N2 respectively in nature at N.T.P.
A molecule is the smallest particle of matter which has individual existence.
A molecule may contain atoms of the same element or different elements combined in fixed ratio. Molecule containing atoms of same element is called homo nuclear molecule. Examples are H2, O2, O3, N2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 etc.
Molecule containing atoms of different elements is called hetero nuclear molecule. Examples are H2O, HF, H2SO4, CH4 etc.
Ionic compounds have no molecules. They have oppositely charged ions and each ion will be surrounded by a group of oppositely charged ion. For them the ratio between the oppositely charged ions is taken as the formula of the molecule. Examples are NaCl has Na+1 & Cl-1 ions in (1:1) ratio. Similarly in CaF2, the ratio between ‘Ca+2’ and ‘Cl-1 ions is 1:2.
In covalent crystals every atom is connected to other by covalent bond, example in Carborundum the ratio between ‘Si’ atoms and ‘C’ atoms is 1:1. Then the molecule formula is taken as ‘SiC’
Some important points about elements:
1 .Aluminium is the most abundant metal in the earth’s crust, it is never found free in nature. All of the earth’s aluminium has combined with other elements to form compounds.
2. Diamond is the hardest non-metal. SILICON CARBIDE is the hardest artificial non-metal. The only compound of silicon and carbon is silicon carbide (SiC), or carborundum. SiC does occur naturally as the mineral moissanite, but this is extremely rare. However, it has been mass produced in powder form for use as an abrasive since 1893.
3. The densest metal found naturally on earth is Osmium. It is a very rare element that is usually found in trace amounts within platinum ores. According to the experimental calculations of density using the x-ray crystallography (X-ray diffraction data) Osmium is the densest stable element with a density of 22.59 g/cm³.
Mercury has the highest density at standard temperature and pressure,
4. Many chemical elements are named after places. Examples of elements named for countries include americium (America), francium (France), germanium (Germany), nihonium (Japan or Nihon), and polonium (Poland).
5. Tin (50Sn) is the element with the greatest number of stable isotopes (ten; three of them are potentially radioactive but have not been observed to decay).
Most total isotopes – stable and radioactive – then it is a tie. Both Xenon and Cesium have 36 possible isotopes.
6. Lithium cannot be stored in kerosene oil , because it is the lightest metal and it floats on its surface and react with air . Therefore it is kept wrapped in paraffin wax.
7. Sodium Potassium also.Lithium metals are stored in kerosene. It is because they react vigorously with oxygen of air, catches fire and start burning when kept open in the air.
8. Mercury (metal) and bromine (non-metal) exist in liquid state at room temperature. Caesium and gallium are metals with melting point less than 310 K.
9. Mercury, francium, cesium, gallium, and rubidium are all metals that are liquid below or near room temperature. Francium is radioactive and cesium and rubidium are both explosively reactive, so these materials are typically avoided.
10. Silver: The single most conductive metal, silver conducts heat and electricity efficiently thanks to its unique crystal structure and single valence electron. followed by copper, gold and Aluminium.
11. Copper, silver and gold are the three metals that are used for making coins and are called coinage metals.
12. Because of their high degree of toxicity, arsenic, cadmium, chromium, lead, and mercury rank among the priority metals that are of public health significance. These metallic elements are considered systemic toxicants that are known to induce multiple organ damage, even at lower levels of exposure.
13. Two of the non metals show lustre they are diamond and Iodine. So we can conclude that Iodine is a lustrous non-metal.
14. H+ The smallest cation in the periodic table.
15. Cs+ has highest ionic radii as it is on the extreme right corner of the table. So it is highest in it’s period and highest in the group.
16. Liquid non meta is ‘Bromine’.
17. Most ductile metal is ‘Gold’. Silver, platinum and copper also are more ductile metals.
18. The 5 Most Precious Metals on Earth crust are Rhodium, Gold, Silver, Platinum, and Palladium.
Compound:
A compound consists of atoms of different elements combined in fixed ratio by weight
In compounds the component elements will not retain their original properties. They lose their original properties and get new properties. Consider water molecule which is made up of ‘H’ & ‘O’ elements. Both of them will lose their original properties and get new properties that of water. For example if you put a burning splinter in ‘H2’ gas pop sound is produced and if you put a burning splinter in ‘O2’ gas it burns brilliantly. If you put a burning splinter in water it puts off and no pop sound either.
In compounds the component elements will always be present in fixed proportion by weight.
In compounds the component elements cannot be separated by physical methods.
For example take water molecule (H2O) in which ‘H’ and ‘O’ will be present in 2:16 = 1:8 ratio by weight.
For example take carbon dioxide molecule (CO2) in which ‘C’ and ‘O’ will be present in 12:32 = 3:8 ratio by weight.
For example take methane molecule (CH4) in which ‘C’ and ‘H’ will be present in 12:4 = 3:1 ratio by weight.
Only atoms can take part in chemical reactions. Molecules split into atoms when they take part in chemical reactions.
What is a mixture? – It contains two or more substances in any proportion by weight. They may be elements, compounds or both. The components do not lose their individual properties.
For example consider sugar solution which has both sugar and water. It is sweet like sugar and liquid like water.
In a mixture the components can be separated by normal physical methods.
| Sr.no. | Homogenous mixture | Heterogenous mixture |
| 1. | A homogenous mixture is that mixture in which the components mix with each other and its composition is uniform throughout the solution. | A heterogenous mixture is that mixture in which the composition is not uniform throughout and different components are observed. |
| 2. | Components of homogeneous mixture cannot be seen through naked eyes. | Components of heterogeneous mixtures can be seen through naked eyes. |
| 3. | In this mixture the component sizes are atomic/molecular level. | Here, in this mixture, the size of particles are large. |
| 4. | Components of homogeneous mixture cannot be separated easily. | Components of heterogeneous mixture can be separated easily. |
| 5. | The constituent particles in a homogeneous mixture possess the same physical properties. | The constituent particles in heterogeneous mixture possess different physical properties. |
| 6. | Example: salt solution, sugar solution, air, etc. | Example: mixture of salt and sugar, grains and pulses along with some dirt particles (often stone pieces) etc. |
Additional Information:
1.Colloids are heterogeneous but in appearance they seem to be homogenous because the constituent particles in the mixture are very small – 1 nanometer to 1-micrometer.
2.A mixture of two solids is always heterogeneous.
Note: It is important to understand these basic concepts to build up higher level concepts.
Different Ways of Separating Mixtures
Some of the common techniques used in separating mixtures are as follow:
a) Filtration is a method for separating an insoluble solid from a liquid. When a mixture of sand and water is filtered: the sand stays behind in the filter paper (it becomes the residue) the water passes through the filter paper (it becomes the filtrate)
b) Centrifugation is a technique used for the separation of tiny solid particles from a liquid that can easily pass through a filter paper. Centrifugation is used for carrying out the separation of these insoluble particles where normal filtration fails to work well. The centrifugation depends upon the viscosity of the medium, speed of rotation, shape, size, and density of the particle. This technique is based on the principle that lighter particles stay at the top and heavier or denser particles are forced to move at the bottom when spun rapidly. The apparatus used for the centrifugation technique is called a centrifuge. The centrifuge mainly includes a centrifuge tube holder called a rotary. It holds balanced centrifuge tubes that contain an equal amount of solid-liquid mixtures. Now a days in all laboratories this technique is used in qualitative analysis
c) A separating funnel is mostly used to segregate or separate the components in a mixture two immiscible liquid phases. The mainly aqueous phase and organic solvents are the two immiscible liquid phases found in this method respectively. The mechanism of separation depends upon the unequal density of the liquids. The liquid particles with more density are responsible for forming the lower layer and the upper layer is formed by the liquid having lesser density. This technique is used to separate oil and water.
d) Chromatography
The separation technique is used to separate the mixture components by passing them in the suspension or solution or as a vapor over a medium in which the mixture constitutes or components move at different rates. This technique is dependent on the various properties of compounds present in two phases i.e mobile and stationary phases.
The technique involves dissolving the sample in a specific solvent known as a mobile phase which may be liquid or gas. This specific solvent is then passed over another phase present called a stationary phase. The separation is based upon different speeds at which different components of a mixture travels.
Types of Chromatography
1. Paper Chromatography
2. Thin layer Chromatography (TLC)
3. Column Chromatography
4. Gas Chromatography
e) Evaporation
Evaporation is a method used to separate a solution consisting of a soluble solid and a solvent. The process typically involves heating the solution until the solvent evaporates and no liquid remains behind as it turns into a gas and leaves behind the solid components. In this method solvent is lost as vapour.
f) Simple Distillation
An effective method used to separate a mixture that consists of two or more, miscible liquids using a difference in their boiling points. It is also a purification process in which the components of the liquid mixture with less boiling point vaporizes first and then condensed to collect it. In simple distillation, when the mixture is heated then the most volatile component vaporizes first at a lower temperature. The vapor moves through a cooled tube (condenser) and is collected after it gets condensed into a liquid state. It is called distillate and the one remains in the distillation flask is called still.
g) Fractional Distillation
Fraction distillation is a technique used to separate a mixture that comprises two or more miscible liquids having less difference in their boiling points. All the components will be recovered.
h) Sublimation
Certain substance like iodine, naphthalene, camphor on heating directly changes to vapour state. Such substances can be separated by this method. The mixture containing such substance is taken in a china dish and heated keeping an inverted funnel above the china dish it. The component which sublimes will condense in the inner walls of the funnel.
i) Crystallization
it is a method used to separate the soluble component from the solvent. When the mixture is heated at certain temperature it becomes supersaturated. Then on cooling slowly the solid dissolved separate as crystals.
h) If one of the component in the mixture has magnetic nature using a magnet it can be separated from the mixture. Example iron can be separated from sand.
k) Atmolysis.
This method is based on the difference in the rates of diffusion of the components of the gaseous mixture.
