1. The force of attraction that is binding, atoms or oppositely charged ions together is called chemical bonding.
2. There are two types of chemical bonding ionic and covalent bonding.
3. Electrovalency is proposed by Kossel and Covalency is proposed by Lewis.
4. Ionic bond is formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. It is also called Electrovalent bond.
5. During Ionic bond formation the atom having low I.P, E.N and E.A. values will lose 1 or more electrons and other atom having more I.P, EN and EA values gain one or more electrons. The atom which lost electron or electrons will become cation and its size decreases. The other atom which gained will become anion and its size increases. In between anion and cation the electrostatic forces of attraction existing is called Ionic bonding. Ionic bonding is formed between the following elements generally. s1(1A)group elements & p4 (4A), s1(1A)group elements & p5(5A), s2(2A)group elements & p4 (4A), s2(2A)group elements & p5 (4A),
Transition metals and inners transition models form only, covalent band in higher valency states. On laver state too they form both covalent and ionic bonds.
6. Always unbonded will have more energy than bonded.
7. Electrovalency: The No. of electrons lost or gained by an atom during ionic bond formation is called its electrovalency. Eg: In NaCl electrovalency is +1 & -1 respectively. In Cao electrovalency is +2 & -2 respectively.
8. In the solids of ionic compounds there are no molecules. Every ion is surrounded by a group of oppositely charged ions, so every ion is connected to a group of oppositely charged ions. Hence ionic bonding is non-directional and non-rigid.
10. An orderly three dimensional arrangement of atoms, molecules or oppositely charged ions is called crystal lattice arrangement.
11 Crystals are of 4 types.
a) Ionic crystals: These contain oppositely charged ions arranged in an orderly 3 dimensional manner. The forces of attraction between them are strong electrostatic forces. Eg: NaCl, CsC1,KI ….
b) Molecular crystals: These contain molecules arranged in an orderly 3 dimensional manner.The forces of attraction between them are relatively weak Vander Waals Forces. Eg: Ice, Glucose
c) Covalent Crystals: These contain atoms which are connected to each other by covalent bonds and arranged in an orderly 3 dimensional manner. Eg: Diamond, graphite, carborundum(SiC), B4C3.
d) Metallic Crystals: These contain metal atoms which are arranged in an orderly 3 dimensional manner and the forces of attraction between them weak Electrostatic forces.
12. Hardness, density, M.P. & B.P of various crystals is as follows.
Covalent Crystals > Ionic Crystals > Metallic Crystals > Molecular Crystals.
13. Unit cell: In every crystal there is a smallest repeating unit which is called Unit cell.
Eg: 1. In NaCl every Na+1 is surrounded by 6 C1-1 ions and vice versa. The arrangement is Octahedral or Square bypyramid. Hence the shape of the unit cell is square bypyramid or Octahedral.
2. In CSC1 every ion is surrounded by 8 ions. Therefore the shape of unit cell is CUBE.
14. Coordination number: The number of species surrounding a particular species in crystal lattice arrangement is called coordination number of that species. It can be atom molecule or ion.
Eg: In NaCl coordination No. of Na+ or C1– is 6. In CSC1 coordination No. of Cs+ or C1– is 8.
15. Lattice point: In a crystal, the position of every atom, molecule or ion is called lattice point.
16. There are 230 ways of arranging lattice points. They give rise 14 shapes which are called BRAVIS LATTICES. These are condensed to 7 and they are called Basic Crystal Systems – (1) Cubic (2)Tetragonal (3) Orthorhombic (4) Rhombohedra (5) Monoclinic (6) Triclinic (7) Hexagonal.
17. Cubic Crystal lattice systems are of 3 types.
(a) Simple cube: Where lattice points are at 8 corners of cube.
(b) Face centered cubic lattice (F.C.C): Where lattice points are at the centre of faces. They Can be at places also
(c) Body centered cubic lattice (B.C.C): Where lattice points are at 8 corners and one at the centre of body. Eg: NaCl, KC1, KBr etc. are f.c.c. whereas CsCl,RbC1 etc are b.C.C.
18. Lattice energy (U): It is the amount of energy liberated when 1 mole of a crystal is formed from its gaseous atoms,molecules or oppositely charged ions.
19. Born-Haber cycle is used to calculate the Lattice energy.
20. Usually radius of cation will be less than radius of anion (exceptions RbF, CsF) . The ratio between radius cation (rc) and anion(ra) is called Radius Ratio (R). R = rc/ra,
If R < 0.43 coordination number is 4. If R> 0.43 and < 0.73 coordination number is 6.
If R > 0.73 coordination number is 8. It is called radius ratio effect. (However it is not rigid rule).
21. Whenever two oppositely charged ions approach each other energy decreases. It is calculated as shown here.
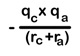
The –ve sign indicates decrease of energy. Here qc and qa are magnitude of charges of cation and anion respectively.
22. If the magnitude of this value is more ‘U’ is more. Stability of crystal is more.
Eg: Among NaF, NaCl, NaBr & NaI, U decreases in the same order because’ rc ‘ is same but ‘ ra ‘ value is increasing.
Eg: NaF, KF, RbF & CaF, U decreases in the same order because radius of anion is same but radius of cation is increasing.
Eg: LiF and MgO have same ( rc + ra ) value but of MgO is more stable because magnitude of charge is more.
Eg: NaF and Cao have same ( rc + ra ) value but CaO is more stable because magnitude of charge is more.
23. Properties of Ionic compounds:
a) In ionic compounds there are no molecules instead there are ions each ion is surrounded by a group of opp. ions. The forces of attraction between them are strong electrostatic forces, which are very strong, hence they possess more M.P. and B.P. density and hardness ‘compared to covalent compounds.
b) c) In solids ions have no movement so they do not conduct electricity and heat. In molten state or in solutions they conduct electricity because ions get freedom of movement.
c) Capacity to weaken the electrostatic forces is called Dielectric constant. It is a measure of a substance’s ability to insulate charges from each other. Solvent having it is called polar solvent. Ionic compounds arc soluble in polar solvents. If polarity of the solvent is more solubility is more.
d) Ions in ionic compounds respond their tests only in molten state or in solutions because ions get movement.
e) When ionic compounds dissolve in water or any polar solvent two changes take place (i) crystal lattice breaks and ions gets separate by absorbing lattice energy (+U) (ii) Ions will be surrounded by solvent molecules liberating solvation energy (-s).
If U > S dissolution is endothermic and solubility is less.
If U < S dissolution is exothermic and solubility is more.
If the solvent is water S is called Hydration energy (H)
f) Ionic compounds do not exhibit isomerismbecause ionic bond is a non directional bond.
Covalent bond or electron pair bond:
24. Covalent bond is formed between atoms whose EN, EA and IP values are equal or nearly equal. It can be formed between Homo and Hetero atoms, whereas ionic bond will be formed only between Hetero atoms.
25. Covalent bond is formed by the sharing of 1 or more electron pairs.26. Covalency is proposed by Lewis. According to him an atom enters into covalent bonding to attain 8 electrons in its valency shell. It is called Octet rule, Except H atom, which attains only doublet.
